Call: 708-425-9080
Welder Qualifications and the ASME Code
 Welder performing gas tungsten arc welding process on stainless steel
Welder performing gas tungsten arc welding process on stainless steel
When reviewing customer specifications and statements of work we generally see either the American Welding Society AWS B2.1 “Specification for Welding Procedure and Performance Qualification” or the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel (B&PV) Code Section IX “Qualification Standard for Welding and Brazing Procedures, Welders, Brazers and Welding and Brazing Operators” referenced as the technical requirement to ensure that welding, weld procedures, and welder qualifications meet quality standards. We have selected the ASME Section IX standard as more appropriate to the fabrication of cryogenic, vacuum and pressure equipment of the type Meyer Tool produces. All our welders are certified to the ASME standard.
Section IX of the ASME B&PV Code sets forth the qualification requirements for welders, brazers, and welding and brazing operators in addition to the procedures they follow in fabricating vessels, components and piping to meet the B&PV Code and also the ASME B31 Code for Pressure Piping. Other sections of the B&PV Code (e.g. Section VIII Pressure Vessels or Section IV Heating Boilers) may state different or additional specifications to the requirements of Section IX; those requirements take precedent for fabrication within that Section.
The majority of welding requirements Meyer Tool encounters while manufacturing in the areas of cryogenic, vacuum, or pressure relate back to either Section VIII Pressure Vessels or B31.3 Process Piping. In order to U Stamp a pressure vessel or certify piping to B31.3 welders must be qualified to the requirements of Section IX. When fabricating pressure or vacuum retaining components not requiring certification, using certified welders ensures quality. This article will discuss the tests required by ASME Section IX to demonstrate and document that welders are qualified to fabricate these types of components.
Section IX of the ASME B&PV Code sets forth the qualification requirements for welders, brazers, and welding and brazing operators in addition to the procedures they follow in fabricating vessels, components and piping to meet the B&PV Code and also the ASME B31 Code for Pressure Piping. Other sections of the B&PV Code (e.g. Section VIII Pressure Vessels or Section IV Heating Boilers) may state different or additional specifications to the requirements of Section IX; those requirements take precedent for fabrication within that Section.
The majority of welding requirements Meyer Tool encounters while manufacturing in the areas of cryogenic, vacuum, or pressure relate back to either Section VIII Pressure Vessels or B31.3 Process Piping. In order to U Stamp a pressure vessel or certify piping to B31.3 welders must be qualified to the requirements of Section IX. When fabricating pressure or vacuum retaining components not requiring certification, using certified welders ensures quality. This article will discuss the tests required by ASME Section IX to demonstrate and document that welders are qualified to fabricate these types of components.
Qualification Process (Weld Coupons / WPS)
Welders are qualified through the testing of weld coupons. Weld coupons are produced in accordance with the requirements of a Weld Procedure Specification (WPS). Other variables are defined by the physical characteristics of the weld coupon and the manner in which it is welded to determine the limits of the welder’s qualification.
A WPS is a standard operating procedure developed by the manufacturer that provides the welder with instructions for producing welds that will meet all Code requirements. The WPS defines the conditions and limits under which a weld may be performed. ASME Code Section IX defines specific “essential variables” for the weld processes (methods used to achieve the weld joint, for e.g. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), Plasma Arc Welding (PAW), etc.) allowed by the Code. The WPS must define these variables within the limits allowed. As mentioned previously, other Sections of the Code may require additional requirements. The most common of these in cryogenic applications is meeting the notch toughness requirements of Appendix UHA as referenced in Section VIII. The manufacturer must develop these WPS first. WPS documents how the welder goes about meeting the required weld quality, not the skill of the welder in achieving that quality.
The WPS must also be qualified. Again this is done through the production of test coupons. A Procedure Qualification Record (PQR) records the actual values of the essential variables and any other information that manufacturer wishes to document during the performance of the test coupons used to qualify the WPS.
A WPS is a standard operating procedure developed by the manufacturer that provides the welder with instructions for producing welds that will meet all Code requirements. The WPS defines the conditions and limits under which a weld may be performed. ASME Code Section IX defines specific “essential variables” for the weld processes (methods used to achieve the weld joint, for e.g. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), Plasma Arc Welding (PAW), etc.) allowed by the Code. The WPS must define these variables within the limits allowed. As mentioned previously, other Sections of the Code may require additional requirements. The most common of these in cryogenic applications is meeting the notch toughness requirements of Appendix UHA as referenced in Section VIII. The manufacturer must develop these WPS first. WPS documents how the welder goes about meeting the required weld quality, not the skill of the welder in achieving that quality.
The WPS must also be qualified. Again this is done through the production of test coupons. A Procedure Qualification Record (PQR) records the actual values of the essential variables and any other information that manufacturer wishes to document during the performance of the test coupons used to qualify the WPS.
Welder Requirements
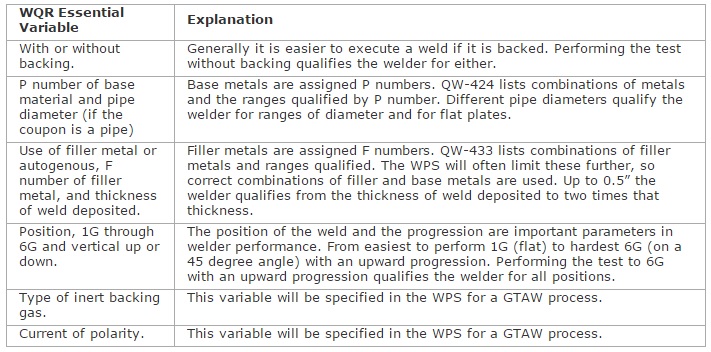
Article III of Section IX defines the requirements for welder qualification. Essential variables that apply to the welder qualification test are listed by weld process. It is important to note that if a welder qualifies to one WPS using a specific welding process the welder is also qualified to the manufacturer’s other WPS using that same process within the limits of the essential variables. The most common welding process Meyer Tool employs in the fabrication of cryogenic, vacuum, and pressure equipment is the Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) processes. The essential variables for welder qualification as defined by Section IX for this process are:
Weld Coupon Requirements
The WPS also defines essential variables or limits that the welder must meet during performance of the weld coupons.
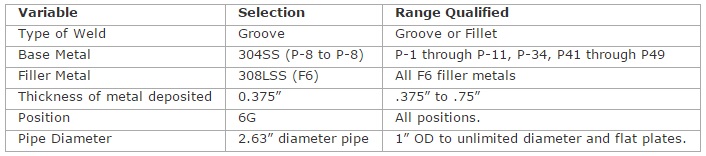
The Code is set up such that through judicious selection of the essential and non-essential variables utilized in producing a weld coupon, the welder can be qualified for a wide range of situations. A series of tables in Section IX define these ranges. Using the GTAW process again as our example, if we define the test coupon requirements as follows, we see the following qualification limits for a welder:
The Code is set up such that through judicious selection of the essential and non-essential variables utilized in producing a weld coupon, the welder can be qualified for a wide range of situations. A series of tables in Section IX define these ranges. Using the GTAW process again as our example, if we define the test coupon requirements as follows, we see the following qualification limits for a welder:
All weld coupons must be visually inspected and undergo either mechanical testing or radiographic testing to assess their acceptability. The welder’s qualification range and the results of the coupon test are documented on a Welder Qualification Record (QWR) form.
Depending upon the skill and experience of the welder, he or she will have multiple QWR forms. For example, to qualify to the full range of Meyer Tool’s WPS for cryogenic welding of stainless steel, GTAW-SS/LT, a welder would have to perform at minimum nine (9) qualification tests.
Depending upon the skill and experience of the welder, he or she will have multiple QWR forms. For example, to qualify to the full range of Meyer Tool’s WPS for cryogenic welding of stainless steel, GTAW-SS/LT, a welder would have to perform at minimum nine (9) qualification tests.
J2394 - Aerospace Grade AWS D17.1 Class A Aluminum Welding WPS Sample QualificationWelding Aluminum is incredibly challenging and requires the skills of an experienced craftsman to produce a weld that is free from defects while maintaining the structural integrity of the material. This video shows you an overview of the process required to create a weld coupon required to qualify a weld procedure. Weld technique, machine settings, and weld prep are designed in such a way to achieve the project requirements. A weld coupon is created using the weld procedure and it is sent out for testing. Testing confirms that the procedure accomplishes its intended goal.
|
|
Meyer Tool Experience
Ensuring the skill level of those performing critical manufacturing processes is of key importance. Welding is a critical process; the procedures and personnel used to perform welding should be qualified to a national standard. Meyer Tool reduces your Project Risk in order to achieve the Lowest Total Cost of Ownership by certifying our welders to the stringent requirements of Section IX of the ASME B&PV Code. We are capable of tackling your toughest welding challenges. We have a database of approved weld procedures and we are capable of creating new weld procedures specific to your applications.